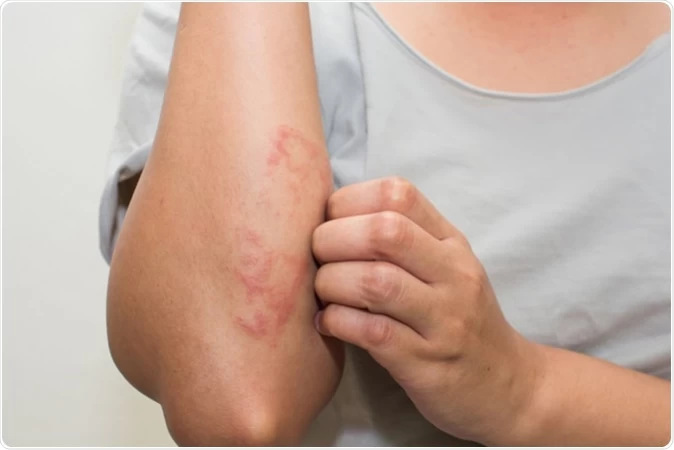
Overview and Meaning of Eczema
Eczema (Atopic dermatitis) is a problem that causes the skin to turn red and itchy. It is common in kids but can happen at any age. Atopic dermatitis is a long-lasting (chronic) disease and tends to flare regularly. Asthma or hay fever may accompany it.
No cure for atopic dermatitis has been identified. But treatments and measures of self-care can help relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks. For example, it helps avoid harsh soaps, Hydrate the skin properly using moisturizer, and use medicated creams or ointments.
The best dermatologist in Jaipur, provide eczema treatments that restore not just the skin but also the self-esteem and social life!
Symptoms
Signs and signs of eczema differ in no small extent and include the following/:
- Dry skin
- Thickened, cracked, scaly skin
- Itching which can be severe, particularly at night
- patches that range from Red to brownish-gray in color, especially on the face and scalp, eyelids, upper chest, neck, the hands, feet, wrists, ankles, in the bend of the knees and elbows, and infants
- Raw, sensitive, swollen skin as a result of scratching
- Raised bumps that are small in size which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched.
Atopic dermatitis most commonly starts before age five and may persist in adolescence and adulthood. It flares periodically to some people, and then clears up for a while, even for a few years.

When you must see the doctor
Consult the best dermatologist in Jaipur if your child or you:
- Are in pain so powerful that the disorder affects the everyday activities and the sleep
- Have inflammation of the skin-check for red lines, pus, scabs yellow in color.
- Still have symptoms despite attempts at-home remedies.
Whether the rash looks infectious and he or she has a fever,seek immediate medical attention for your child.
Causes
Healthy skin helps with moisture retention and protects against bacteria, irritants, and allergens. Eczema is related to a variation of the gene that affects the skin's ability to provide that protection. This allows the environmental factors, irritants, and allergens to affect your skin.
Allergies to foodstuffs may lead to eczema in some children.
Risk factors
The primary and essential risk factor for atopic dermatitis is having a personal or family history of eczema, allergies, hay fever, or asthma.
Complications
Complications of atopic dermatitis (eczema) may include:
- Asthma and hay fever. Sometimes eczema precedes those conditions. Over half of kids with atopic dermatitis develop asthma and hay fever by age 13.
- Chronic itchy, scaly skin. A skin condition called neurodermatitis begins with a patch of itchy skin. You scratch the area, making it all the itchier. Ultimately you can scratch out of habit. This condition may cause the skin concerned to become discolored, leathery, and thick.
- Skin infections. Break open of the skin due to repeated scratching can cause cracks and open sores. These increase the risk of bacterial and viral infections, including the herpes simplex virus.
- Irritant hand dermatitis. This affects people in particular, whose work requires their hands to be often wet and exposed to harsh soaps, detergents, and disinfectants.
- Dermatitis is caused by allergic contact. This condition is common in those suffering from atopic dermatitis.
- Problems in sleeping.The itch-scratch cycle can cause the low quality of sleep.
Prevention
The following tips can help prevent dermatitis bouts (flares) and minimize the bathing's drying effects:
- Hydrate and Moisturize your skin at least twice a day. In the moisture seal creams, ointments and lotions. Choose a product which suits you well. Using petroleum jelly on your baby's skin will help prevent the development of eczema.
- Try to find causes that exacerbate the disease, and prevent them. Things that can make the skin's reaction worse include sweat, stress, obesity, soaps, detergents, dust, and pollen. Reduce your Triggers exposure.
- Children and infants may experience flares from eating certain foods, such as eggs, milk, soy, and wheat. Talk to your child's doctor about identifying any possible allergies to food.
- Take shorter baths or showers. Limit your showers and baths to 10 to 15 minutes. And use warm or lukewarm water instead of hot.
- Use only gentle soaps. Choose mild soaps. Deodorant soaps and antibacterial soaps remove more natural oils and will make it dry.
- Dry yourself carefully. Using a soft towel after bathing, gently pat your skin dry and apply moisturizer when your skin is still damp.
Diagnosis
The identification of atopic dermatitis (eczema) requires no lab test. Your health care provider would likely decide by examining your skin and your medical history. Patch testing or other tests can also be used to rule out other skin disorders or classify eczema-related conditions.
If you suspect that a particular food has caused a rash to your child, tell the top dermatologist in Jaipur and ask to identify potential food allergies.
Treatment
Atopic dermatitis has the potential to persist. To control it, you may need to try different treatments over months or years. And although treatment is successful, there may be signs and symptoms (flare) returning.
Recognizing the condition early is essential, so you can begin treatment. If regular moisturizing and other self-care procedures do not help, a dermatologist in Jaipur near me may recommend one or more than one of the below-mentioned treatments:
Medications
- Creams that suppress itching and assist in skin repair. Your health care provider can prescribe a corticosteroid cream or an ointment. After you moisturize apply it as directed. Overuse of this medicine can lead to side effects, including thinning skin.
- Drugs to fight infection. If you have a bacterial infection, open sore, or cracks in your skin, a dermatologist in Jaipur may prescribe an antibiotic cream. He or she can suggest that you take oral antibiotics for a brief period to treat the infection.
- Oral drugs that help in controlling inflammation. Your doctor can prescribe oral corticosteroids for more severe cases-such as prednisone. These drugs are successful, but they can't be used for the long term because of their severe side effects.
Therapies
- Wet dressings. Effective, intensive treatment for serious atopic dermatitis includes the wrapping of topical corticosteroids and wet bandages into the affected region. This is often performed with people with extensive lesions in a hospital since it is labor-intensive and requires nursing skills. Or, ask your dermatologist in Jaipur to find out how to perform this procedure at home.
- Light therapy. This therapeutic procedure is used for people who either do not get better with topical treatments or who, after the process, easily flare up again. The simplest method of light therapy (phototherapy) involves exposing the skin to natural sunlight in controlled quantities. Other types use artificial ultraviolet A (UVA) and narrow ultraviolet band B (UVB), either alone or with medicine.
While successful, long-term light therapy can have adverse effects, including premature skin aging and increased skin cancer risk. Phototherapy is less widely used in young children for these reasons and is not offered to babies. Talk to your health care practitioner regarding the ups and downs of light therapy.
- Counseling. Talking to a therapist or other psychologist may help depressed people with their skin condition or upset.
- Relaxation, behavior modification, and biofeedback. These approaches can help people who habitually itch.
Conclusion
Though a topical condition that's only skin deep, eczema can penetrate deep into the individual's psyche by giving them the inferiority complexes that nobody desires.
A dermatologist in Jaipur ensures that your confidence is restored. Treatment for eczema done using various therapies aims to ensure that you gain your self-confidence back and treat your skin for the condition.